Photoresists & Specialty Chemicals
Permanent Epoxy Photoresist for Pixel Grids in Electrowetting
Part of the Applications Notes Line
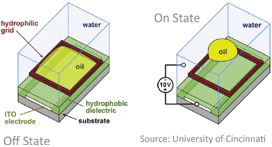
In electrowetting, liquid surface tensions are modified by applying a field potential. With no voltage applied, colored oil lies flat between water and the electrode within a defined well. When a voltage is applied between the electrode and water, the tension changes and the water then forces the oil aside.
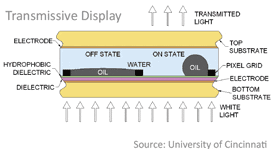
In electrowetting displays (EWD), the use of an active matrix TFT back-plane can control each pixel allowing for high speed and video content. Because electrowetting is low power, this is an attractive technology for many applications. Electrowetting displays can also be used in both reflective and transmissive modes and offer higher brightness compared with other reflective technologies.
Electrowetting is also used for a wide range of microfluidic lab-on-chip applications.
SU-8: Benefits/Attributes
- Highly crosslinked system with high structural strength
- High contrast with vertical sidewalls
- High aspect ratio imaging
- High fill factor pixel walls
- Ability to adhere to fluoropolymers
- Fast photospeeds for high volume manufacture
SU-8 Pixel Walls with oil shown in the on, mid and off state

Transmissive display using an SU-8 Grid
Courtesy of University of Cincinnati, Plastics Electronics 2010
SU-8 Material Properties>
| Dielectric Constant | 4.1 @ 1GHz |
| Volume Resistance | 2.8×1016Ω/cm |
| Surface Resistance | 1.8×1917Ω/cm |
SU-8 2000 Pixel Walls
Source: Kayaku Advanced Materials, Inc. Applications Lab
SU-8 2000 Pixel Walls
Source: Kayaku Advanced Materials, Inc. Applications Lab
FEATURED APPLICATIONS