Photoresists & Specialty Chemicals
Waveguides
Part of the Applications Notes Line
Waveguides used at optical frequencies are typically a dielectric structure, e.g. SU-8 or PMMA, with high transmission and high index of refraction surrounded by a material with lower %T. The structure guides optical waves by total internal reflection.
Integrated optics/photonics is becoming more pervasive as devices communicate with one another. Low optical loss is an important consideration for any waveguide fabrication technique. Optical losses in waveguides arise due to the material absorption and scattering losses from the sidewalls. The former is intrinsic to a particular material while the latter is attributed to the lithographic process. The refractive indices of the waveguide core, cladding and substrate are essential input parameters necessary to predict system behavior. Above a wavelength of 400 nm, the transmission of SU-8 is greater than 95%. SU-8 is optically transparent at 632.8 nm as well as at the telecommunications wavelengths of 1330 nm and 1550 nm. SU-8 is therefore a suitable material for optical waveguides. A sensor/detector waveguide stripe interferometer can be formed from SU-8 with a reactive clad coating that changes optical properties upon interaction with the substance to be detected.
PMMA and SU-8: Benefits/Attributes
- Excellent adhesion
- Optical transparency
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Spin coatable
- Material compatibility

Sensor structure – waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Made of SU-8 photolithography deposited stripe waveguides. Source: M. Bednorz, Silesian U Molecular and Quantum Acoustics vol. 27, (2006)
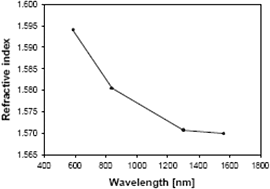
Refractive index of SU-8 film as a function of wavelength. Source: U. of Twente, NL
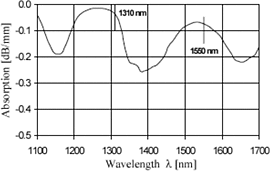
PMMA NIR-range Abs.; the two telecommunication λs are indicated. Source: Karlsruhe Institute for Mat. Res.
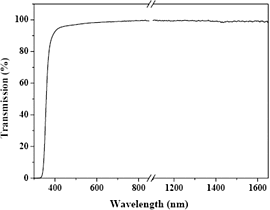
Transmission vs. wavelength spectrum of cross-linked SU-8 resist. Only the data from the visible wavelengths (400 nm to 800 nm) and the communications wavelengths (1330 nm & 1550 nm) are shown. Source: Investigation of SU-8 Waveguides, Cpt. 5






